When configuring your device’s internet connection, you’ll see several fields under APN settings, including one labeled Port. This field, when used, defines the port number for the proxy server responsible for routing mobile data. Below, you’ll find a comprehensive guide to the Port field in APN settings and how it might impact your internet connection.
Quick Summary
The Port in APN settings is the numeric identifier that allows your device to connect to your carrier’s or MVNO’s proxy server. While many carriers leave this field blank by default, knowing how and why to specify a port can help you troubleshoot data connection issues and optimize certain applications, such as VPNs or custom data routes.
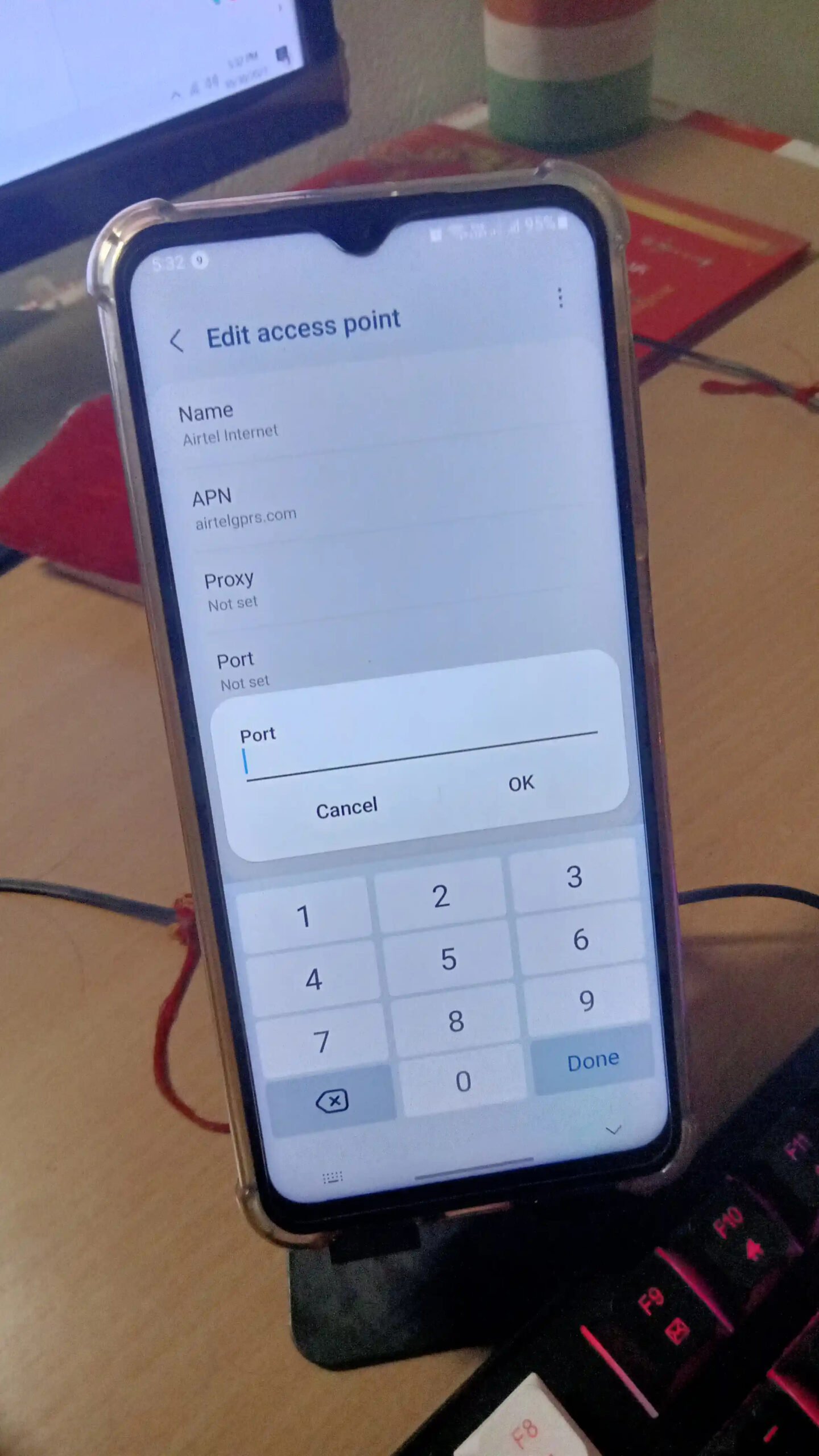
Why it matters: Your phone communicates with the mobile network’s proxy server through a specific port. If this port is incorrect or blocked by a firewall, you risk losing internet connectivity or limiting your access to certain apps or sites.
Key Facts About the Port Field
| Field | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | The Port number used to communicate with the proxy server specified in your APN settings. |
| Examples | 8080, 3128, 443, 8888, 8000 |
| Necessity | Mandatory only if your carrier requires a proxy server for data routing; otherwise, it can often remain blank. |
| Common Defaults | 8080 and 3128 are frequently used for HTTP; 443 is used for secure connections (HTTPS). |
| Role in Troubleshooting | An incorrect or blocked Port number can lead to broken or erratic data connections, requiring you to either select an alternate port or remove the proxy server setting entirely. |
| Carrier-Specific | Each carrier may have a unique port requirement. It’s best to check official documentation or confirm with customer support. |
| Roaming Impact | While roaming, some carriers may use additional or different proxy settings, including alternate port numbers. |
When Should You Adjust the Port?
You may need to modify the Port field if:
- You are unable to access specific services or apps (e.g., streaming platforms, messaging apps).
- Your carrier publishes a new proxy and port to handle updated network architecture.
- A VPN client or security app requests that you enter a custom port for data routing.
- You observe persistent connection failures or frequent timeouts when loading websites.
Step-by-Step: Editing the Port in APN Settings
While interfaces vary by device, these 7 steps generally apply:
- Open your device’s Settings menu.
- Navigate to Mobile Networks or Cellular Networks.
- Select Access Point Names (APNs).
- Tap the APN you want to modify.
- Scroll to find Port.
- Enter the port number provided by your carrier (for example, 8080 or 443).
- Tap Save, then restart your device if prompted.
After these steps, verify your connectivity by opening a web browser or testing the app you were initially having trouble with.
Common Ports and Their Typical Uses
Below are 5 widely used ports you may see in APN settings:
If your device or carrier recommends a port not listed above, it’s still valid—these are just the most common ones. Remember, there are 65,535 possible ports, but only a fraction is typically used for web and carrier proxy traffic.
Troubleshooting APN Port Issues
- Can’t connect to the internet? Double-check the Port and Proxy settings against your carrier’s official documentation.
- Some sites load, others don’t? Verify if the port is restricted or blocked by your network or a firewall application.
- Switching carriers or roaming? Confirm whether the roaming carrier uses different Port/Proxy details.
- Using a VPN? Some VPNs function only on specific ports—enter the port number the VPN provider requires.
In certain cases, removing the port entirely (or leaving it blank) might restore connectivity if your carrier doesn’t require a proxy server.
Port Forwarding vs. APN Port
Port Forwarding is a separate concept more common in home or office networks. It involves redirecting incoming traffic on a specific port to a device or service (e.g., hosting game servers) within your LAN. By contrast, the Port in your APN settings deals with how your device’s mobile data traffic is routed through the carrier’s network. Both involve numbered ports, but their application and configuration steps differ significantly.
Conclusion
The Port field in APN settings can seem obscure, but it’s essential for devices using a proxy server to reach the internet. If your carrier requires a custom port, entering it accurately can mean the difference between seamless connectivity and no data at all. By verifying the correct port—often 8080, 443, or 3128—you can avoid many connection problems. When in doubt, consult official carrier resources to ensure you have the right proxy and port values. A small edit in this field can lead to a big improvement in overall data reliability.
