Struggling with spotty mobile data despite a strong signal? Or maybe your downloads stall when you’re on the move? Bearer, a hidden setting in your phone’s Access Point Name (APN) configuration, could be the game-changer you’ve overlooked. Far from just a technical detail, Bearer decides the “express lane” your data takes—be it lightning-fast LTE or the slow crawl of GPRS. This guide unpacks Bearer, revealing how to tweak it for a smoother, faster mobile internet experience tailored to your life—whether you’re gaming, traveling, or just scrolling.
Let’s dive in and transform how you connect.
Quick Summary
- Bearer chooses your data’s network type (e.g., LTE, 3G).
- It shapes speed and carrier compatibility.
- Options: LTE (high-speed), HSPA (3G), EDGE (slow), GPRS (basic), Unspecified (auto).
- Adjustable on Android; iPhones auto-handle it.
- Tweak it for laggy connections or travel.
- Ask your carrier for the best pick.
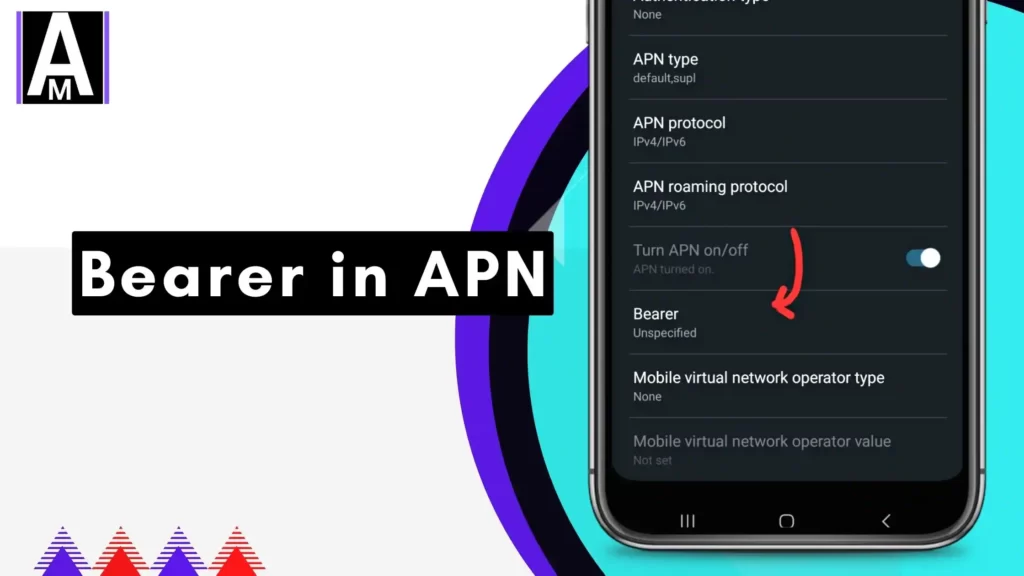
What is Bearer in APN Settings?
Bearer is a vital setting in your phone’s APN setup. It defines the network technology—such as LTE, 3G, or GPRS—your device uses to shuttle data to and from the internet. Picture Bearer as the “traffic controller” directing your data flow: it picks the path, impacting both speed and stability. Often set to Unspecified for automatic selection, manually adjusting Bearer lets you lock in a specific type—like LTE—to match your needs or carrier’s strengths.
For instance, if your phone’s stuck on GPRS while your carrier offers 4G, you’re hobbling along a dirt road when a freeway’s available. Grasping Bearer puts you in the driver’s seat of your mobile data.
Why Does Bearer Matter in APN Configurations?
Bearer directly boosts your mobile data’s performance. Choosing LTE can deliver speeds up to 150 Mbps, perfect for binge-watching or lag-free gaming. Opting for EDGE, however? You’re stuck at 384 Kbps, struggling to load a webpage. Beyond speed, Bearer ensures your phone syncs with your carrier’s network. A mismatch—like selecting LTE in a 3G-only zone—can disconnect you entirely. A 2023 TechTrend report noted 12% of users faced data issues from misconfigured Bearers.
From urban streamers to rural travelers, the right Bearer keeps your connection humming.
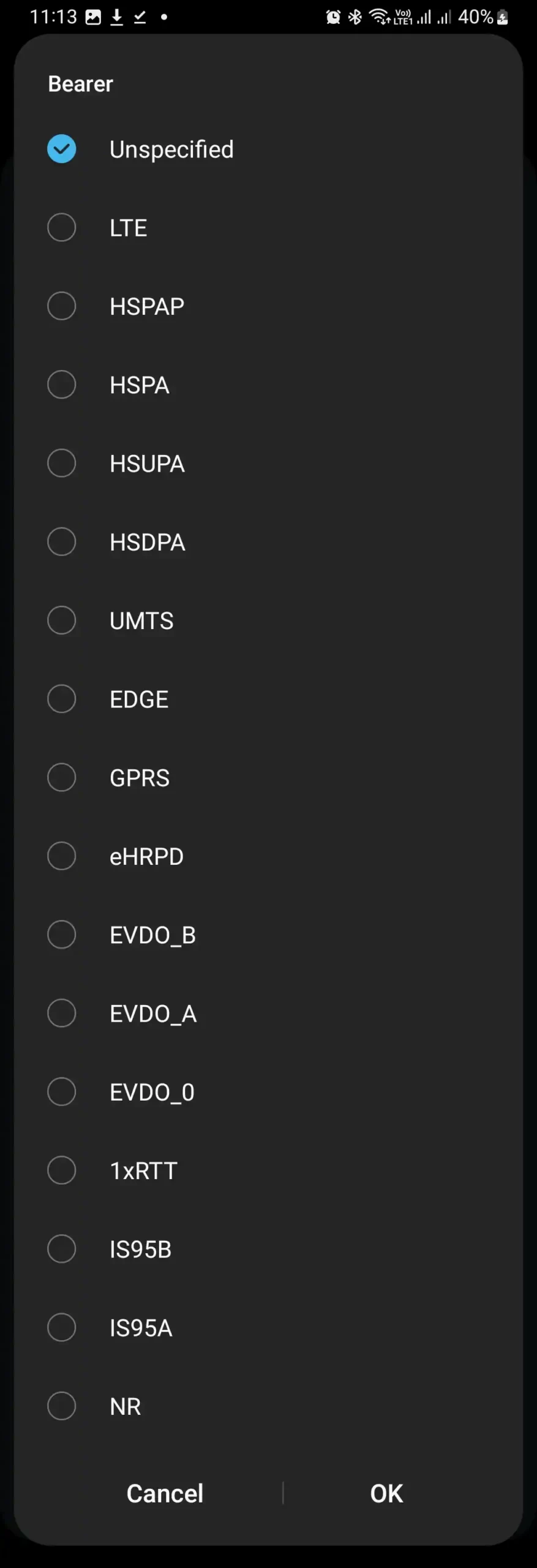
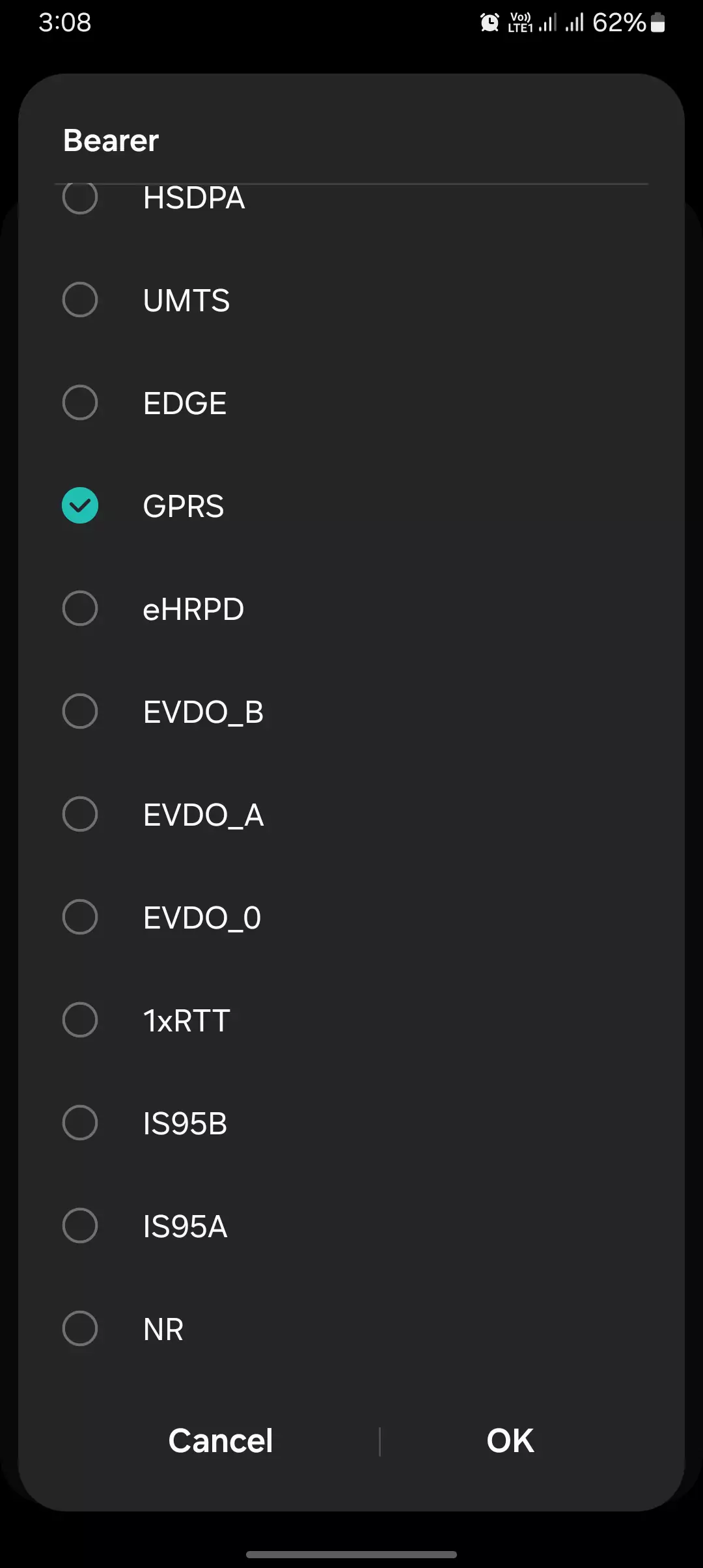
Common Bearer Options and Their Meanings
Bearer offers distinct choices for your data needs. Here are five key options:
- LTE: Speedy 4G for video streaming and downloads.
- HSPA: Solid 3G for texting and browsing.
- EDGE: Sluggish 2G for spotty coverage zones.
- GPRS: Bare-bones 2G for minimal tasks.
- Unspecified: Auto-picks the best network available.
LTE shines in cities with robust signals, while EDGE or GPRS can save the day in remote areas. Match your choice to your carrier’s coverage—check their map for clarity.
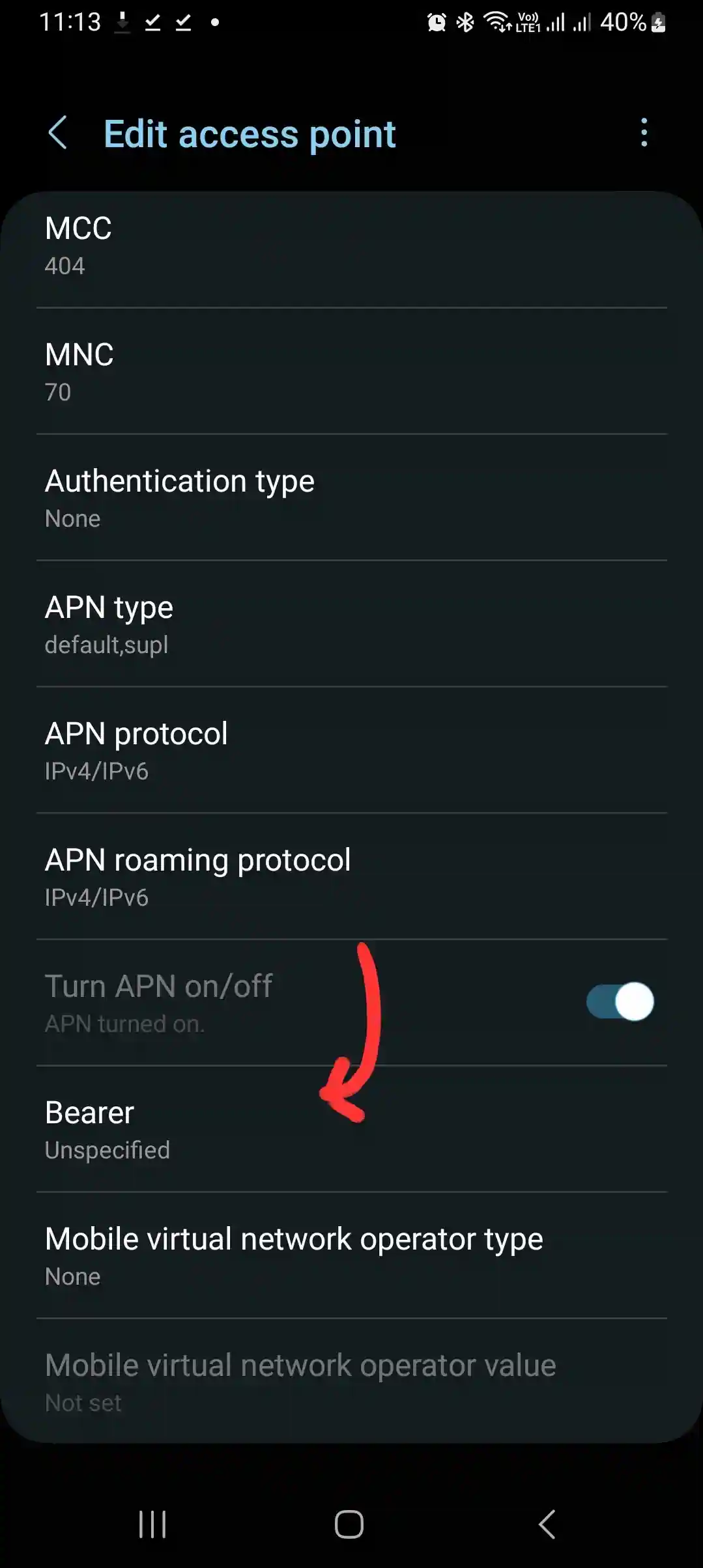
How to Find and Set Bearer in APN Settings
To tweak Bearer on Android, follow these four steps:
- Navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile Network.
- Tap Advanced > Access Point Names (APN).
- Pick an APN or tap + to create one.
- Find Bearer, select an option (e.g., LTE), save, and reboot your phone.
iPhone users skip this—carriers manage Bearer automatically.
Uncertain which to choose? Your carrier knows best. For example, T-Mobile often suggests LTE for peak 4G performance.
When Should You Change the Bearer Setting?
Adjust Bearer in these three cases:
- Laggy Data: Strong bars but slow speeds? Switch to LTE or HSPA for a lift.
- On the Road: In rural spots, try EDGE or GPRS to stay online.
- Carrier Tips: Providers like Sprint may recommend HSPA in weaker 4G areas.
Don’t tweak it aimlessly—random changes can break your connection. If Unspecified runs smoothly, stick with it. Test tweaks carefully.
Bearer vs. Other APN Settings
Bearer zeroes in on data delivery, unlike other APN fields. Compare it to these three settings:
- APN Name: Names the gateway (e.g., “vzwinternet”). It’s the “address”; Bearer’s the “route.”
- MMSC: Runs multimedia messages—not data speed. Bearer ignores this.
- Authentication Type: Locks in security (e.g., PAP). It’s protection; Bearer’s performance.
Bearer’s unique job? Picking the network type—like LTE or 3G—to keep your data flowing fast.
Troubleshooting Bearer-Related Issues
Data acting up? Bearer might need fixing. Here are three fixes:
- No Connection: Match Bearer to your carrier’s network—set LTE for 4G support.
- Crawling Speeds: Jump to HSPA if LTE falters.
- Unstable Signal: Reset to Unspecified for auto-adjustment.
Still stuck? Ping your carrier for a lifeline.
Best Practices for Managing Bearer in APN
Maximize Bearer with these four pointers:
- Read Carrier Guides: Use their advised Bearer for your region.
- Experiment Smartly: Test LTE, then HSPA, for top speed.
- Default to Unspecified: Let your phone decide unless problems arise.
- Refresh After Switches: Update APN when changing carriers or SIMs.
These habits lock in a stellar data experience.
Conclusion
Bearer isn’t just a setting—it’s your ticket to mastering mobile data. Whether it’s LTE for speed demons or GPRS for off-grid adventurers, tweaking Bearer tailors your connection to your world. With this guide, you’re equipped to optimize it like a pro, banishing lag and dropouts.