When setting up APN (Access Point Name) settings, most users focus on internet speed and carrier compatibility but often overlook one crucial element—APN authentication type. This setting determines how your phone, tablet, or IoT device authenticates with the carrier network, affecting data access, security, and network stability.
Many users experience mobile data issues like slow speeds, authentication failures, or even blocked APNs without realizing that the wrong authentication type could be the cause. Whether you’re configuring T-Mobile’s APN settings or setting up a 5G eSIM, understanding authentication methods is essential.
This guide explores PAP, CHAP, and certificate-based authentication, their impact on network security, and how they integrate with 5G, MVNOs, IoT, and private networks.
Quick Summary
- APN authentication ensures secure data connections between your device and your carrier.
- Three authentication types exist: PAP (basic), CHAP (encrypted challenge-response), and Certificate-based (high-security for IoT/5G).
- PAP is vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks, while CHAP improves security but is still based on MD5 hashing, which can be cracked.
- 5G networks, IoT devices, and enterprise systems are shifting towards certificate-based authentication for better encryption and security.
- Incorrect APN authentication settings can result in no internet access, dropped connections, or slow speeds.
For those wondering, “What happens if my APN is not set properly?”, read this guide to understand the risks.
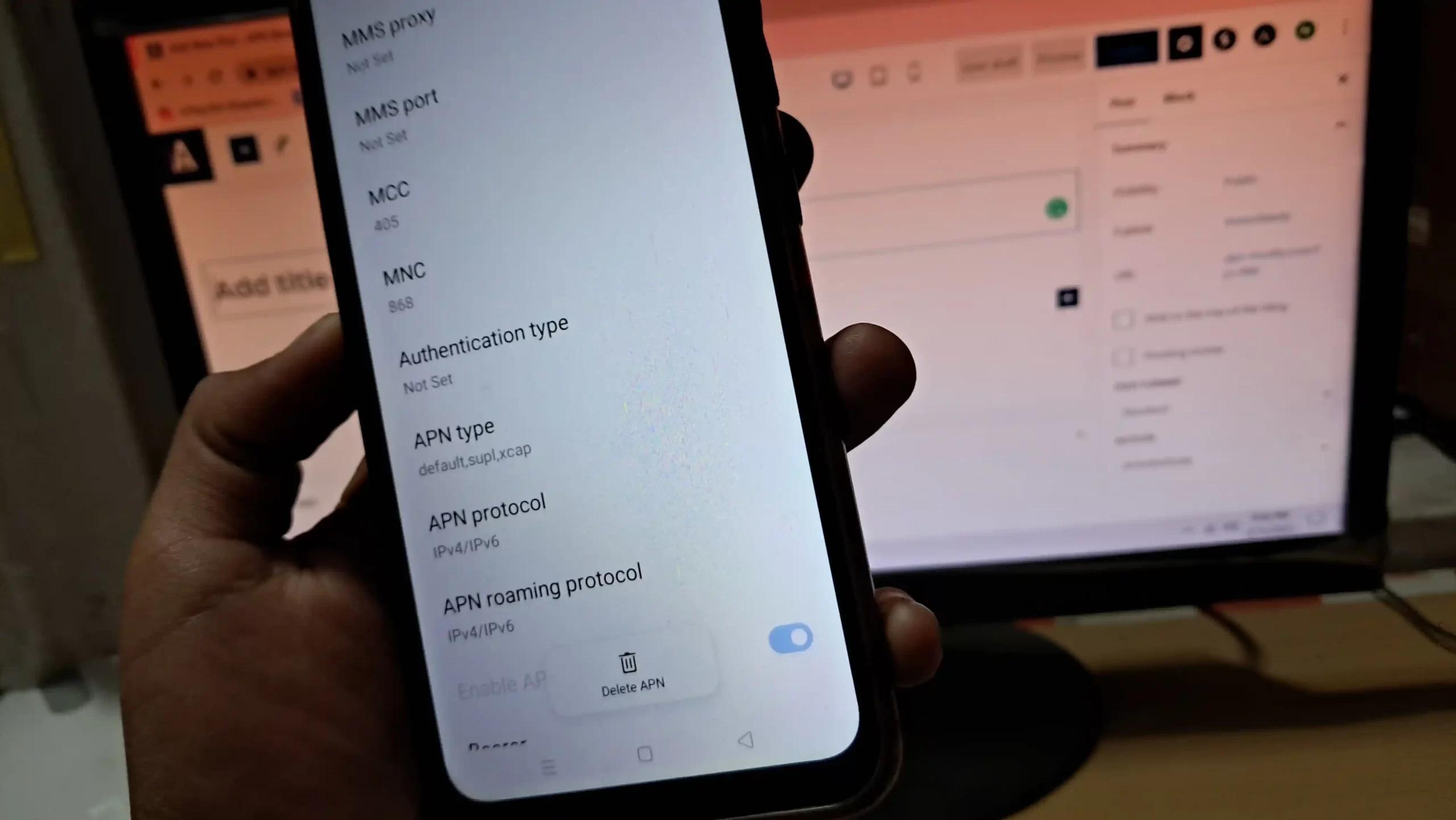
1. What is APN Authentication?
APN authentication is the process of verifying your device’s identity before it is granted access to mobile data. This prevents unauthorized devices from connecting to a carrier’s network and ensures secure internet and data communication.
Why Does APN Authentication Matter?
- Protects your mobile data from unauthorized access.
- Ensures MVNOs and prepaid networks can control who connects and how they are charged.
- Improves mobile security, preventing SIM hijacking, spoofing, and network abuse.
- Essential for VoLTE, tethering, and mobile hotspot functionality (Check USB tethering guide).
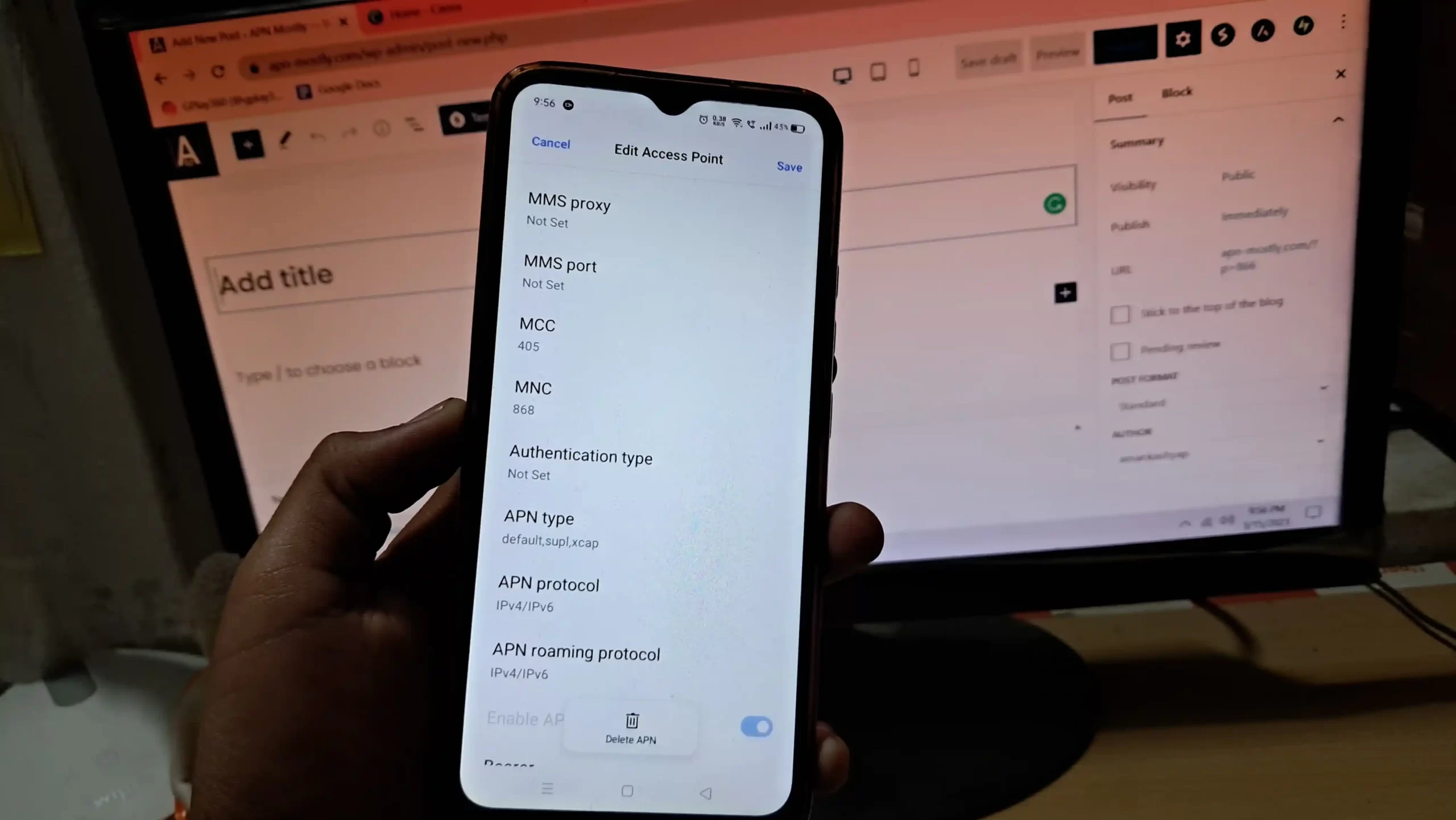
For a deeper look into how APN settings impact mobile connectivity, check out the comprehensive APN guide here.
2. Types of APN Authentication
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
How it Works:
- PAP sends the username and password in plain text over the network.
- No encryption, making it vulnerable to MITM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks.
Security Risks:
- Easy to intercept, especially on public Wi-Fi or unsecured networks.
- Used mainly in legacy systems and prepaid SIMs with minimal security concerns.
Use Cases:
- Prepaid MVNOs like Mint Mobile, Ting Mobile, and Ultra Mobile (Fastest APN settings for Ultra Mobile).
- Older IoT devices with low-security requirements.
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol)
How it Works:
- Uses a challenge-response mechanism where passwords are hashed before transmission.
- More secure than PAP, but still vulnerable to brute-force attacks on MD5 hashes.
Security Benefits Over PAP:
- Prevents replay attacks (attackers can’t reuse authentication messages).
- Encrypts password transmission, reducing the risk of theft.
Use Cases:
- Enterprise mobile networks with enhanced security.
- VoLTE authentication, ensuring high-speed LTE calls work properly.
- APN security in roaming networks (Check data roaming guide).
Certificate-Based Authentication (Used in 5G & IoT)
How it Works:
- Uses digital certificates stored on SIM/eSIM to authenticate devices.
- The carrier verifies certificates instead of passwords.
Advantages:
- High-level security for IoT and 5G network slicing.
- Eliminates the risk of password theft or brute-force attacks.
Use Cases:
- 5G network slicing for enterprise and industrial automation.
- eSIM-based devices (Learn how eSIMs work).
- Smart city deployments requiring secure APN authentication.
3. How to Change Authentication Type in APN Settings
On Android:
- Go to: Settings → Network & Internet → Mobile Networks → Access Point Names (APN).
- Select an APN or create a new one.
- Look for the “Authentication Type” field (may be listed as PAP/CHAP).
- Choose PAP, CHAP, or None based on carrier settings.
- Save and restart your phone.
On iPhone:
- Most iPhones lock APN authentication settings via carrier profiles.
- If manual changes are allowed, go to:
- Settings → Cellular → Cellular Data Network → Authentication Type.
- If APN settings aren’t available, check this guide on finding APN settings on iPhone.
4. Common APN Authentication Issues and Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No internet access | Incorrect APN authentication type | Change to PAP or CHAP based on carrier |
| VoLTE not working | CHAP authentication not supported | Switch to PAP or certificate-based authentication |
| Slow data speeds | PAP authentication fails during congestion | Request CHAP from carrier for better stability |
| 5G data not connecting | APN authentication mismatch with network slicing | Ensure certificate-based authentication is enabled |
5. Advanced APN Authentication Troubleshooting
Using Wireshark to Analyze Authentication Handshakes
- Filter network packets using gsm_sim to check CHAP/PAP authentication failures.
- Look for rejected hash values, indicating incorrect passwords or authentication blocks.
Carrier-Specific Authentication Requirements
- T-Mobile USA: Uses PAP for general users but switches to CHAP for enterprise VoLTE.
- Verizon 5G Slices: Requires certificate-based authentication instead of legacy PAP/CHAP (Check Verizon APN settings).
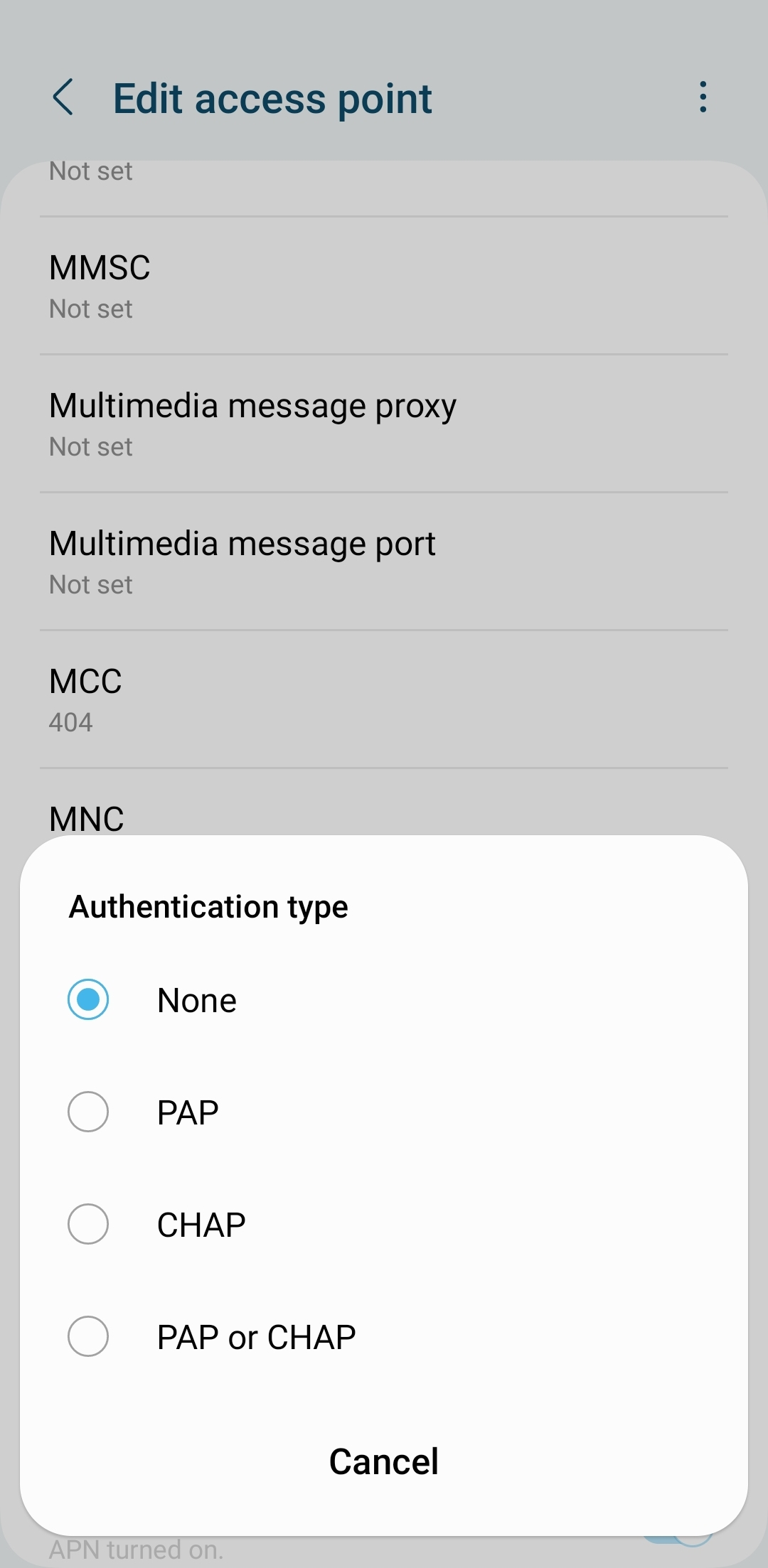
6. Future Trends in APN Authentication
- Quantum-Safe Authentication for APNs
- 5G and 6G networks are moving towards quantum-resistant encryption for APN authentication.
- Post-quantum cryptography like CRYSTALS-Kyber is being explored for securing mobile networks.
- eSIM and Remote APN Provisioning
- eSIM profiles automatically configure authentication settings, reducing errors in enterprise IoT.
- Eliminates manual APN setup and simplifies carrier switching.
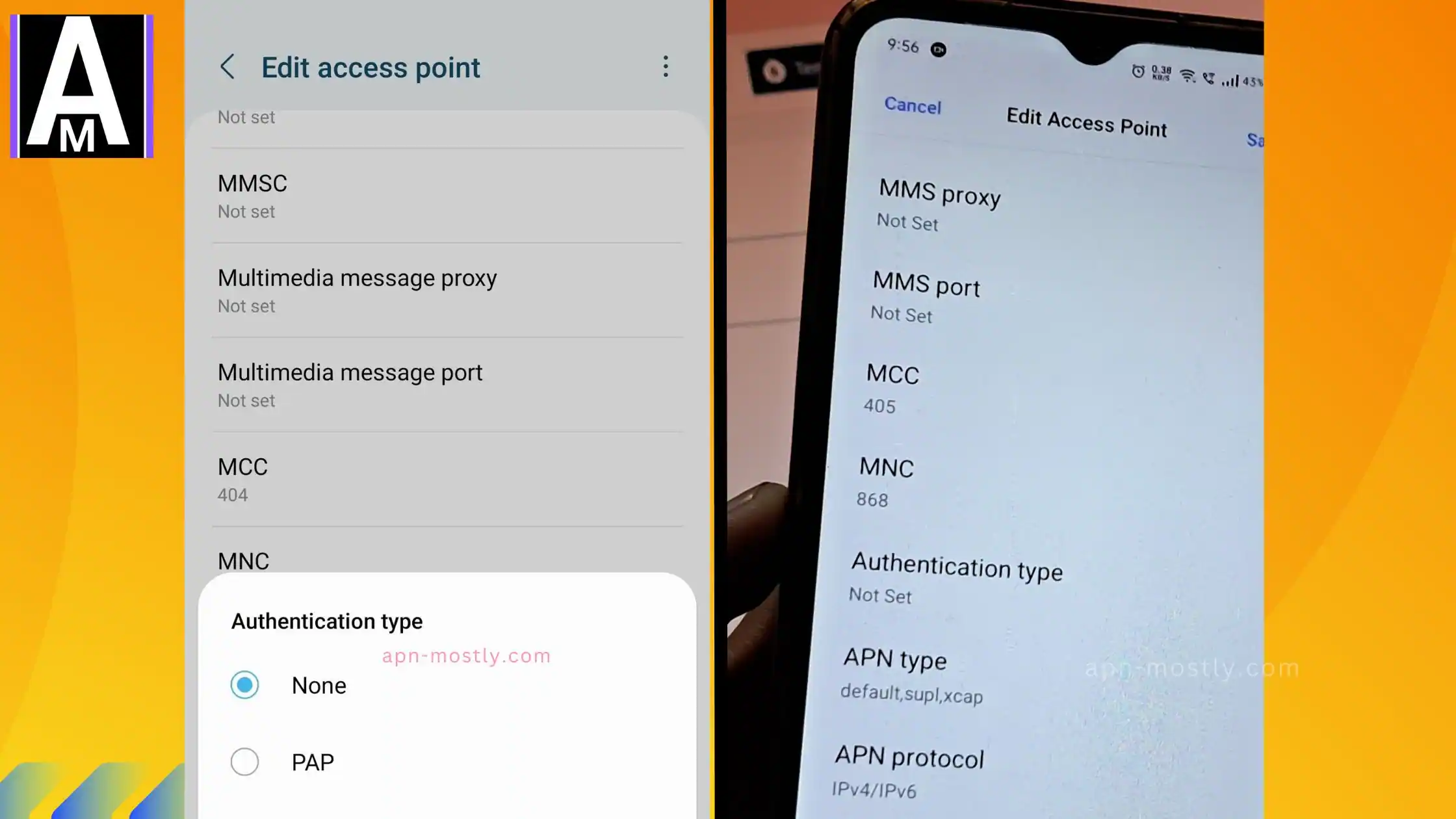
Conclusion
Choosing the correct APN authentication type is critical for mobile network security, connectivity, and performance. Whether using PAP, CHAP, or certificate-based authentication, always ensure your APN settings are configured properly.
Key Takeaways:
- Always use the recommended authentication type based on your carrier’s requirements.
- CHAP is more secure than PAP, but certificate-based authentication is the future.
- Incorrect authentication settings cause network failures, slow speeds, and blocked APNs.
- 5G, IoT, and eSIM devices require stronger authentication methods beyond traditional PAP/CHAP.
For more detailed APN troubleshooting, check the full APN settings guide. 🚀
